What are pacemakers?
Pacemakers are devices that can be placed in your body, usually by surgery, to support the electrical system in your heart. They can stabilize abnormal heart rhythms and prevent problems that can disrupt or endanger your life.
How do pacemakers work?
Your heart has its own electrical system, which tells your heart’s chambers when it’s their turn to squeeze. When your heart’s electrical system malfunctions, your heart’s chambers may squeeze in the wrong order or squeeze too weakly to provide enough blood to your body. Pacemakers use electrical impulses to correct these kinds of malfunctions.
What conditions do pacemakers treat?
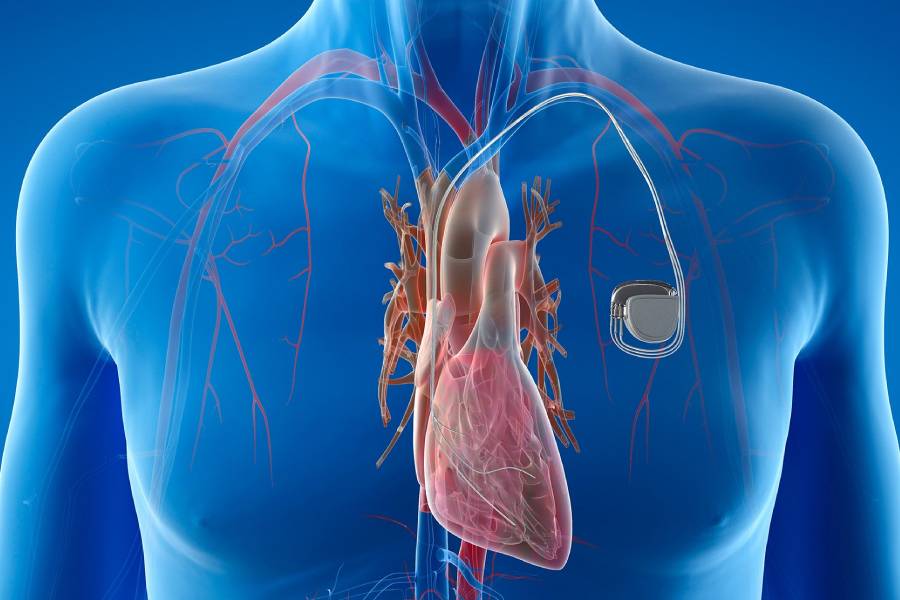
Conditions that are treatable with a pacemaker include (but aren’t limited to):
- Certain heart arrhythmias (malfunctions of your heart’s normal beating process).
- Disruptions of your heart’s electrical system (such as heart blocks).
- Heart failure.
- History of a heart attack.
What are the signs you need a pacemaker?
Talking to your healthcare provider about your concerns or symptoms is the first step to determining if you have health problems that can be treated with a pacemaker. Some of the symptoms you should tell your healthcare provider about include:
- Chest pain (also known as angina).
- Tachycardia: This is an unusually fast heartbeat (more than 100 beats per minute).
- Bradycardia: This is an unusually slow heartbeat (fewer than 60 beats per minute).
- Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia): A heartbeat that skips beats or adds in extra beats.
- Heart palpitations: This happens when you can feel your heartbeat in a way that’s unpleasant (it might feel like your heart is “flip-flopping” or pounding in your chest).
- Shortness of breath, especially when you’re more active.
- Unexplained dizziness or lightheadedness, nausea or fainting.
- Unexplained confusion.
- Swelling in your ankles, legs and abdomen.
- Needing to urinate multiple times at night.
What are the different types of pacemakers?
Depending on the heart problem, a specific type of pacemaker — with anywhere from one to three wires (called leads) — may be used. Types of pacemakers include:
- Leadless pacemaker: A small pacemaker (about the size of a large pill) inserted using a catheter-based procedure. This device is attached to the inner wall of your heart, which means it doesn’t need to use any wires.
- Single-chamber pacemaker: Uses a single wire attached to one chamber of your heart.
- Dual-chamber pacemaker: Uses two wires attached to two chambers of your heart.
- Biventricular pacemaker: Uses three wires, two of which attach to the lower chambers (called ventricles) of your heart, and a third connected to the right upper chamber (the right atrium). This is also known as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
What are the possible benefits?
Pacemakers are meant to improve your quality of life and prevent disruptions caused by heart problems. Benefits include:
- Alleviating many of the symptoms caused by heart rhythm problems, including chest pain, confusion, palpitations, nausea, confusion and more.
- Preventing unpleasant symptoms like fainting that are caused by arrhythmias.
- Saving your life by preventing your heart from stopping.
Looking For Permanant Pacemaker in Ahmednagar?
Dr. Dhananjay Ware provides the best pacemaker in Ahmednagar. For more information about our comprehensive treatment options, or to request an appointment with the best cardiologist in Nagar call 96576 13635 or Click on Book Appointment for online booking with your near hospital.
